Application of HPC Tools for the Optimization of 3D-printed Orthopaedic Devices
Presentation of the problem and objective of the experiment
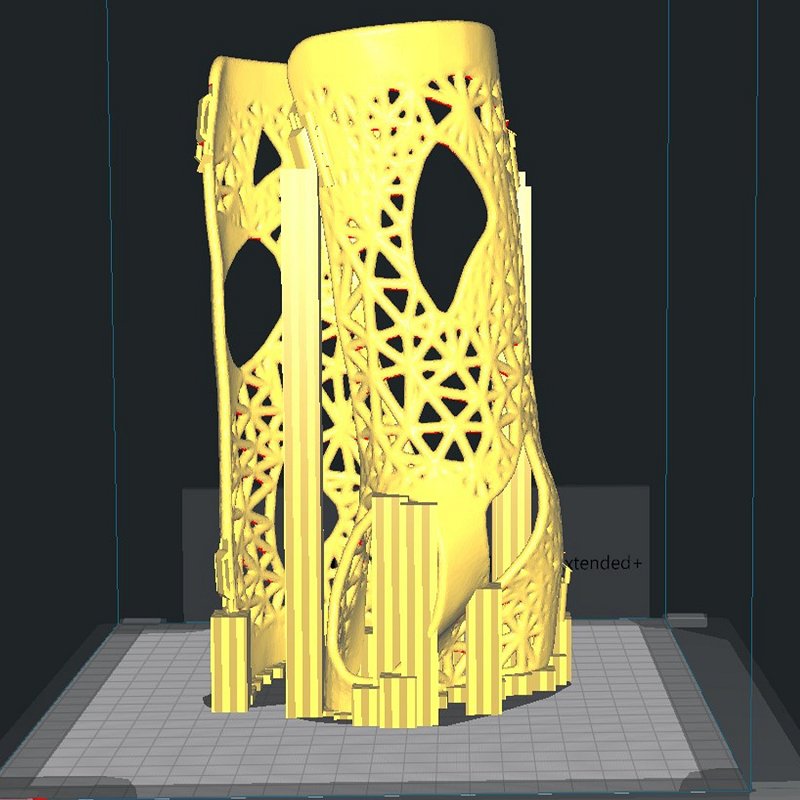
3D printed parts are used in orthopedics and prosthesis production to reduce device weight. CastPrint, in cooperation with doctors, is uniquely solving immobilization of fractures (without dislocation), for example, replacing traditional plaster with an individually made lightweight, safe, waterproof, and ventilating 3D printed cast. The biggest challenge in scaling and exporting the CastPrint service abroad is maintaining high precision and quality of 3D designs of the assistive devices at a rapid increase in demand both locally and abroad.
Short description of the experiment
Incorporation of HPC tools in the manufacturing process of CastPrint products to reduce printing time and material, increase mechanical strength and wearability through increased ventilation of the cast. This will be achieved by using topological optimization of the product's geometry. As the scanned models usually include 3-5 million surface elements, topological optimization of the desired geometry is computationally intensive. Therefore, the application of HPC technology is needed to provide CastPrint with a tool that can be incorporated into the workflow of the company’s manufacturing process. The work plan includes practical yield stress tests with the improved product. All tests and calculations will be focused on wrist fixators.
Organisations involved:
End User: CastPrint SIA
Expert: Institute of Numerical Modelling, University of Latvia
HPC Centre: Riga Technical University
Partners Riga Technical University and Institute of Numerical Modelling, University of Latvia are part of the NCC Latvia.