Cloud-Based CFD Optimization of Magnetic Drive Pumps using HPC
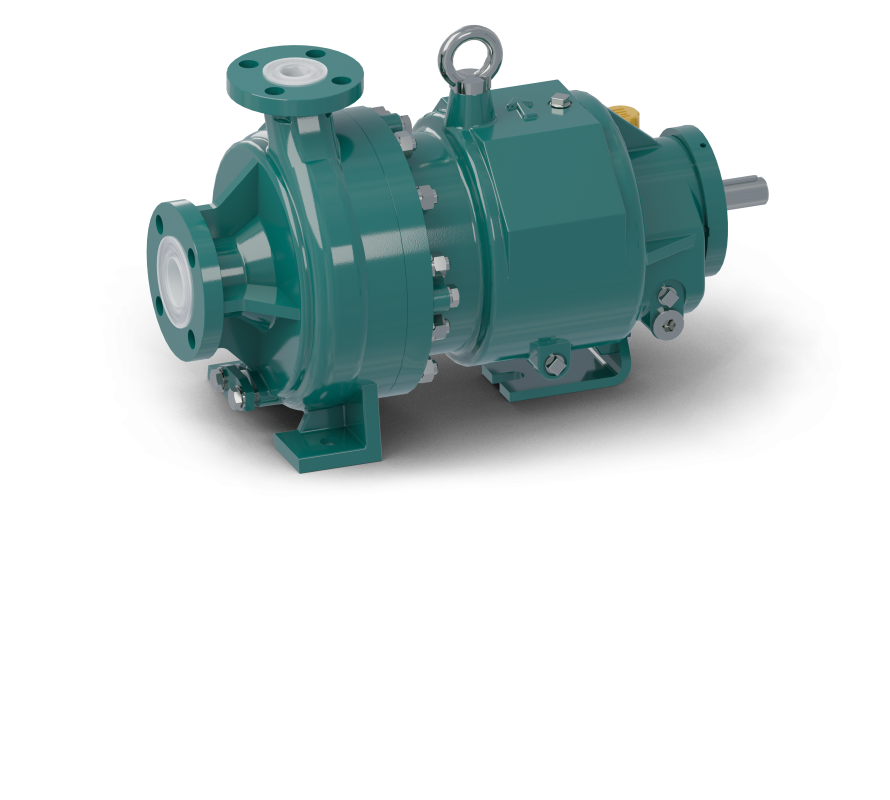
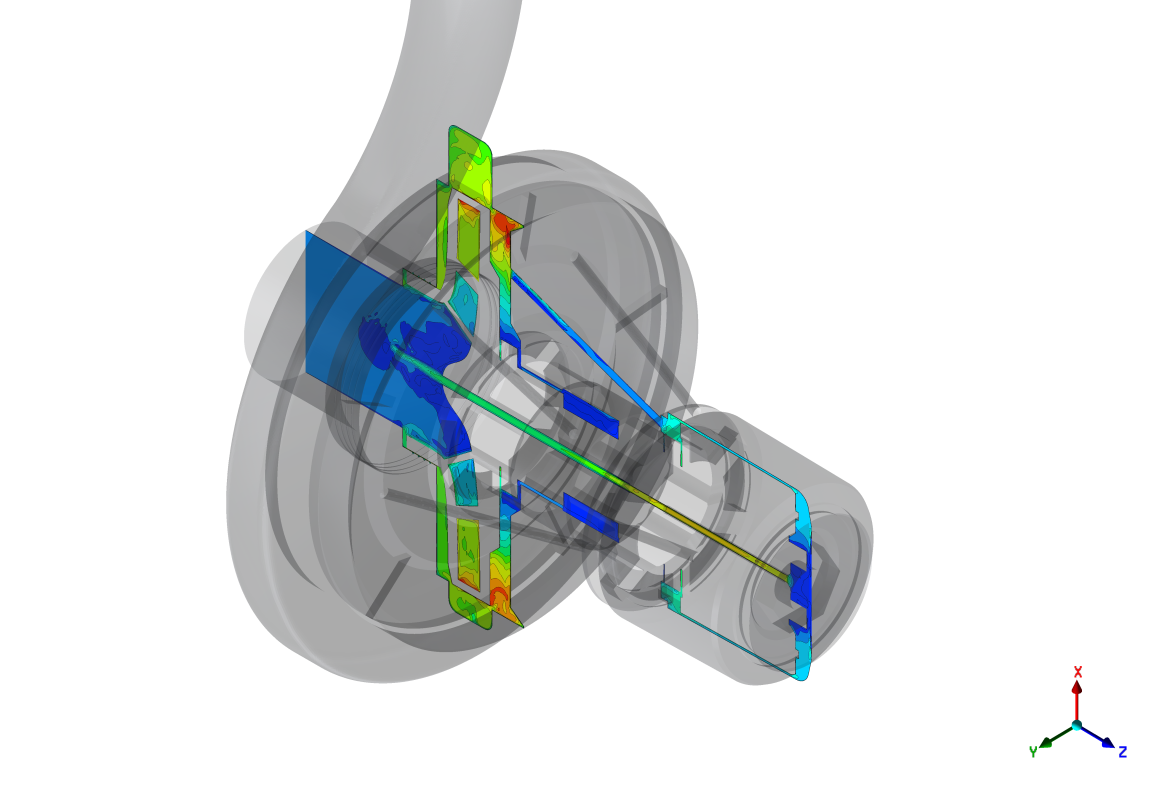
The experiment investigated and optimized magnetic-drive centrifugal pumps using Cloud-based HPC with the objective of improving performance and developing new products. Mag-drive chemical-process pumps eliminate the need for shaft sealing, reducing costs. Axial thrust balancing is critical for the design: CFD allows this to be predicted, but the optimization of the pumps to maximize efficiency, minimize thrust and avoid cavitation requires very large models. Thus, advanced HPC infrastructure and CFD engineering tools are essential.
SECTOR: Manufacturing
TECHNOLOGY USED: HPC, CFD Simulations
COUNTRY: Italy
The Challange
Magnetic drive chemical-process pumps eliminate the need for shaft sealing, which reduces costs while improving safety. These pumps are used to avoid leakage of aggressive fluids such as those found in the chemical, pharmaceutical, or nuclear industries.
CDR strongly desired to re-design four sizes of this kind of pump in order to improve product performance and reduce both engineering and manufacturing costs, and to comply with regulations on markets outside Europe, while delivering more efficient and more competitive products. In particular, the following improvements were seen as most pressing:
- Minimising axial force (to avoid too much thrust against the delicate internal components, which could lead to early failure of the machine with the related consequences);
- Minimising cavitation and thereby decreasing the Net Positive Suction Head required (NPSH), or increasing the operating range and flexibility of use by decreasing the suction pressure necessary to ensure proper pump operation;
- Reducing energy consumption;
- Finding a compromise between the previous targets and higher efficiency, which can be solved with a constrained multi-objective optimisation through Pareto improvements (when more outputs in terms of performance are optimised simultaneously).
However, the simulation tools, know-how, and HPC infrastructure required for these design improvements were not available to CDR.
The solution
In the experiment, CDR teamed up with EnginSoft to employ CFD modelling and optimisation for the four pump sizes to find the best compromise between geometry fidelity, accuracy, and computational costs.
The advanced tuning of the CFD models led to a high-fidelity steady-state approach with an adequate CFD grid resolution (30-70M elements), which guaranteed the result accuracy. The subsequent geometry-based optimisation process, built on top of the CFD model, was based on the Design of Experiment and Response Surface methodology. It enable delivery, for each pump size, of optimised performance maps in terms of head, efficiency, power, NPSH (reduced by 20-25%, reducing risk of cavitation and erosion of blades) and axial thrust (reduced by 5-20%, permitting longer pump lifetime). In total 130,000 core hours were used to investigate more than 80 design points for each pump size. The results particularly increase the ability to operate the pumps in extreme situations expected to be critical, such as off-design conditions at the limit of cavitation, and provide a good balance between efficiency and thrust.
Thus, the target objectives have been successfully fulfilled from the technical point of view, while providing CDR with a new working methodology and knowledge that will be useful to improve further pump designs.
Business impact, social impact, environmental impact
- Substantially improved energy efficiency, lifetime, and robustness of CDR’s magnetic pump models.
- Improvements enable access to the US market for CDR Pompe (the US and North American market in global terms is the primary market in volume for centrifugal pumps and the market segment with higher potential is in CDR’s field of application. In 2021 the US pump market size was USD 12 Billion).
- EUR 1.5M additional annual turnover expected after 5 years for CDR.
EUR 1.5M additional turnover in the pump design sector is expected for EnginSoft in the next 3 years.
Organisations involved:
End User: CDR Pompe S.r.l.
Domain Expert: EnginSoft S.p.A.
HPC Provider: CINECA